The development of the European social model rests on the concept of social entrepreneurship. The concept has a significant contribution to the development of the European social economy. Social entrepreneurship has a remarkable potential, through its innovative solutions, to play an indispensable role in the social cohesion of EU Member States. The development of social economy in the EU contributes significantly to employment creation, sustainable growth and a fairer distribution of income and wealth.
Thanks to the social sector it is possible to combine profitability and social inclusion and to achieve correspondence between services and needs in the public and private sectors. It is essential that compared to other sectors this one has demonstrated its economic and social potential to better address the economic crisis. Therefore, it is getting more and more support for development in almost all EU countries. However, there are significant differences in the scope and scale of development of social economy within the European Union.
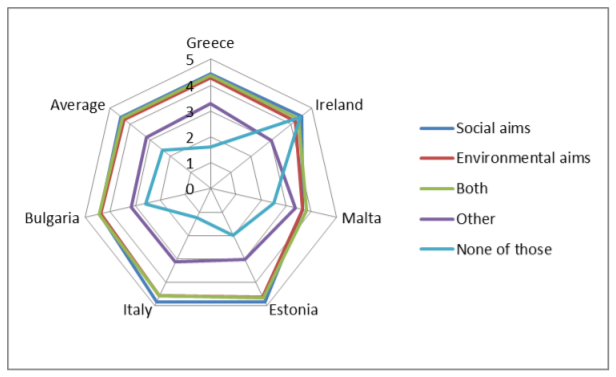
The purpose of this study is to examine the state and development of social entrepreneurship based on different national models in six EU countries. The majority of the study is based on the results of the comparative analysis of experts’ evaluations occupying different positions in the social economy structure of the following European countries: Greece, Bulgaria, Ireland, Italy, Malta and Estonia.
As the current study shows, social economy enterprises in their various forms (including social enterprises) play an important role in boosting the competitiveness and efficiency of the European economy in many different ways: by directing the fragmented and untapped resources towards economic activity; local resources mobilization; enhancing the culture of entrepreneurship; elimination of market rigidities; promotion of market flexibility and production at multiple locations – and these are just some of the examples. Social economy enterprises also have a greater capacity to preserve employment and prevent job loss during difficult stages in economic cycle, as we have seen in the current economic crisis. The number of advantages of social economy enterprises obviously lead to their growth within the EU. This trend is confirmed in the countries surveyed – Bulgaria, Greece, Italy, Ireland, Estonia and Malta.
The results of the survey show that the interest in establishing enterprises with predominantly social objectives and providing social services to vulnerable groups and society in general, is big in EU countries. This interest is particularly strongly expressed in Estonia, Italy and Ireland.
The diverse nature of social economy, as well as its concepts and organizations with different legal forms, are perceived in all surveyed countries, without any particular differences. The establishment of social enterprises identifies and distinguishes those organizations that work within the framework of the statutory standards and are eligible to benefit from policies designed to promote and stimulate social economy and the establishment of social enterprises in cooperation with the private sector (Tepavicharova, Bencheva, 2016d).
Social enterprises require a wide variety of supports in order to maximize their benefit to society and many sectors from Government to the media can help to provide these supports. One particular type of support which is required, however, is that of business advisers who are specifically competent in the kinds of supports and capacity building required by social enterprises.
The social enterprise in the countries surveyed is perceived as a way of doing business. The objectives of social enterprise are often linked to social and/or environmental programs. These are for-profit enterprises but they are created to address social issues; they are aimed at satisfying the needs of the local community or achieving social changes, not just for personal profit. They strive to combine entrepreneurial leadership and innovation – typical of the best of private business practices – with social objectives. They deal with a wide range of social and environmental issues and operate in all areas of the economy.
An important feature is that they pay dividends to shareholders, just as in the private sector. Their aim is to reinvest the profits in order to achieve social goals. Social enterprises have a key role in regeneration and economic development and in the promotion of social inclusion. They provide jobs and services sometimes where the private sector has not entered or has withdrawn, sometimes on behalf of the public sector, and sometimes through a joint venture. Social enterprises in the EU play an essential role in helping to create a strong, sustainable and socially inclusive economy.
Please download the full article text here.
Full reference of this scientific article is here: Vasilyeva, T., Bilan, S., Bagmet, K., & Seliga, R. (2020). INSTITUTIONAL DEVELOPMENT GAP IN THE SOCIAL SECTOR: CROSS-COUNTRY ANALYSIS. Economics & Sociology, 13(1), 271-294.


This publication has been prepared within INDIGISE project. The content of this publication is the sole responsibility of the project coordinator and may not always reflect the views of the European Commission or the National Agency.














Leave A Comment